Tearful toddlers or children on their first day of school are frequently linked to separation anxiety. But childhood isn’t the only time this emotional reaction occurs. According to recent studies↗, 6.6% of individuals may at some time in their life exhibit symptoms typical of separation anxiety.
It is essential to comprehend the incidence and consequences of separation anxiety in the adult population. Adults with separation anxiety may report greater degrees of vocational impairment, according to another study↗. This supports the notion that separation anxiety is an illness that has a substantial influence on a person’s quality of life until it is resolved with the aid of thorough therapy, rather than being a passing emotion.
What Are the Primary Aspects of Separation Anxiety Disorder?
The psychiatric disease known as separation anxiety disorder, or SAD, is typified by an overwhelming worry or anxiety over being separated from the people you are attached to. Babies, parents, lovers, and other people and situations can all produce stress that results in separation anxiety.
Moving far from friends and family or needing to change jobs can also cause separation anxiety. Let’s examine the primary themes of separation anxiety disorder as they relate to adult life below.
Anxiety about Separation vs. Adjustment Disorder
Adjustment disorder, often referred to as stress response syndrome, is a transient illness that describes a situation in which you are unable to manage a certain stressor. Any major life transition, such as the death of a loved one or an especially trying time, might fall under this category.
Anxiety related to adjustment disorders can also affect adults. A sudden change in life, like moving far away for a new work, might set it off. Anxiety symptoms associated with adjustment disorder may intensify if you are separated from your home, friends, family, and support network.
Fear of Being Apart from Your Child
Separation anxiety disorder is very common among parents, particularly new moms. Maternal separation disorder↗ and postpartum separation disorder are other names for this illness. It is common among new mothers. When a parent is separated from their kid, even for a little period of time, they may worry, feel depressed, and feel guilty, which can lead to maternal separation disorder.
Women’s levels of the hormones progesterone and estrogen drop during childbirth. Because of this, they may be more prone to stress, which can lead to intense emotions of dread and panic. Lack of sleep from caring for a baby might intensify these emotions and make matters worse.
Partner Separation Anxiety
It’s natural and rather typical to miss your mate. It’s common to feel lonely and anxious while you’re apart from them and to wish they were back. You may be suffering from separation anxiety from your spouse, though, if your fear, anxiousness, and emotional upheaval become so overwhelming that they interfere with your everyday activities.
There is more to these uneasy sensations than simply missing your companion. They frequently include a more profound fear that you can’t address without them. Separation anxiety also makes you believe that you could lose your lover forever or that they would probably be harmed if you are not with them.
Fear of Being Apart from Pets
Separation anxiety has been seen in pets. Pet owners frequently suffer from separation anxiety disorder, though, if they must be separated from their animals. If you exhibit any of the following symptoms, you may have pet separation anxiety:
- You have an unreasonable concern that your pet may experience an unusual situation. Your pet may hurt itself while you’re away from them, or they may be abducted or murdered.
- You frequently come up with irrational reasons to stay with your dogs and skip work, social gatherings, and time with family and friends. Another option is to demand that your pet accompany you, regardless of how unsuitable the setting or atmosphere may be.
- You worry about your pets, which makes it hard for you to concentrate on your work and other tasks. At work, this may lead to laxity and subpar performance.
What Signs Indicate Adult Separation Anxiety Disorder?
The most common symptoms and indicators of separation anxiety disorder (SAD) are listed below. Although the following list may help you understand the symptoms of SAD, it is imperative that you seek professional assistance rather than self-diagnosing. Thus, the following are typical signs of adult separation disorder:
- heightened anxiety when facing or expecting to be away from home or loved ones.
- worrying excessively about the death of your loved ones and potential damage to them. This might involve worrying about your loved ones being ill, getting into an accident, getting hurt, or passing away.
- steadfastly refusing to leave the house because of a dread of being away from relatives.
- excessive anxiety over being alone yourself or estranged from your family at home.
- recurring dreams in which your core family is apart.
- bodily symptoms that occur frequently when one is apart from important family members. Headaches, nausea, stomachaches, and vomiting are some examples of these physical symptoms.
- clinically significant discomfort or a dread of separation that impairs social, professional, or intellectual functioning.
Excessive worry↗ and possible separation anxiety disorder are indicated by the presence of three or more of the aforementioned symptoms. In toddlers and adolescents, the symptoms continue for around four weeks, whereas in adults, they last for six months or more.

What Are the Causes of Adult Separation Anxiety Disorder?
The reasons of separation anxiety disorder differ from person to person since it is closely linked to personal experiences. Nonetheless, there are recurring trends and elements, like:
- The experiences of childhood. separations or traumatic experiences during early life.
- The chemistry of the brain. anomalies or imbalances in brain structures or neurotransmitters linked to fear and anxiety.
- Events in life. important life changes, such relocating to a new place, losing a loved one, or ending a meaningful relationship.
- Dynamics of relationships. Relationships that are too codependent or entangled lead to a strong dependence on another individual for emotional support.
- Previous traumas. Anxiety over separations might be exacerbated by adult traumas such as betrayal, abandonment, or other experiences.
- Health problems of the body. Anxiety symptoms may be directly brought on by some medical problems, particularly those involving hormone imbalances or brain function.
Which Risk Factors Are There?
A number of risk factors can raise the chance of developing SAD, even if its exact cause is not always known. These consist of:
- Ancestry. Anxiety disorders, including SAD, may be more likely to develop in children whose parents have anxiety disorders or other mental health issues.
- Stressors in life. Separation anxiety can be triggered by stressful events or major life changes, such as a traumatic occurrence, parental divorce, a major loss, or relocating to a new location.
- Extended time apart. SAD risk can be raised by prolonged absence from a major caregiver or loved one, particularly in early infancy. This covers circumstances where the child is separated from their parents, such as hospital stays, boarding school, or extended travel.
- Parents who are overly protective or obtrusive. The risk of SAD may increase if children raised by overprotective parents do not acquire the coping mechanisms needed to deal with separations.
- Problems with attachment. Separation anxiety may be exacerbated by issues in the parent-child attachment process, such as irregular caregiving or disturbances in early bonding.
- Safety or health issues. A person may be more sensitive to separations if they have had past illnesses or experiences that endangered their feeling of stability. Additionally, chronic sickness, particularly in children, can occasionally lead to increased reliance on caregivers, which can exacerbate the grief of separation.
- Character. Youngsters who are inherently shy or timid may be more susceptible to separation anxiety.
- Gender. Although SAD can affect people of any gender, some research↗ indicates that it might affect women more often than men.
What Are the Outcomes of Severe Adult Separation Disorder?
Living a regular life can be difficult for those with separation anxiety disorder and the stress that goes along with it. Additionally, SAD affects the individuals you care about and those in your immediate vicinity. For parents, friends, spouses, or kids, persistent attachment and clinginess might be too much to handle. Therefore, social, marital, and personal areas of your life can all be impacted by an intense separation anxiety condition.
Adults who suffer from separation anxiety disorder may have underlying mental health conditions. More details on its long-term effects may be found here.
SAD’s Impact on Relationships
The effects of separation anxiety frequently impact interpersonal relationships, such as the inability to establish committed and long-lasting love partnerships. Because of your attachment problems, people with SAD run the danger of taking advantage of you in toxic relationships.
Adult separation anxiety disorder typically causes harm to the afflicted individual as well as their relationship. Being too watchful, possessive, and protective might interfere with your partner’s comfort and personal space. As a result, both parties may experience needless disagreements, altercations, and psychological strain.
Personal and Social Disabilities
The following are some ways that adult separation anxiety might impact social, personal, and professional spheres:
- Insufficient initiative and a lack of enthusiasm for cleaning.
- Insufficient involvement and social connection.
- A lack of enthusiasm for learning.
- Mood swings that are irritable and unstable.
- An inability to accept accountability.
- Exceptionally sensitive.
- A decline in productivity.
- Inability to concentrate on duties as provided.
Parental SAD’s effects on kids
Both parents and children are impacted by parental separation anxiety. Children with SAD may continue to experience its affects as adults. People who were raised by parents who struggled with separation anxiety, for example, are more likely to be unindependent as adults.
In addition, the kids could become clinging and defiant as a coping strategy. Because of their overly protective upbringing, the youngster is also more likely to have separation anxiety.
Separation anxiety’s effects on mental health
Your mood might be greatly impacted by a separation anxiety disorder if treatment is not received. Additionally, it can raise the risk of acquiring other mental health conditions including anxiety and depression and result in a persistent dread of abandonment. You have a higher chance of acquiring personality disorders including dependent personality disorder and borderline personality disorder if you have separation anxiety disorder.
How Can Separation Disorder in Adults Be Diagnosed?
A thorough interview that focuses on symptoms, duration, and potential triggers is the first step in diagnosing adult separation anxiety disorder. The DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition) criteria for SAD are compared to this evaluation to make sure that symptoms are severe and last longer than six months. A comprehensive physical check also eliminates illnesses like thyroid issues that could be causing the anxiousness.
Mental health practitioners also investigate the person’s past mental health conditions, early life experiences, and potential traumatic incidents. In order to ensure an accurate diagnosis, the selection of the best course of treatment, and strategies to assist with separation anxiety, they may also watch the patient’s behavior during possible separation scenarios and distinguish symptoms of SAD↗ from disorders that present similarly, such as generalized anxiety disorder, personality disorder, or agoraphobia.
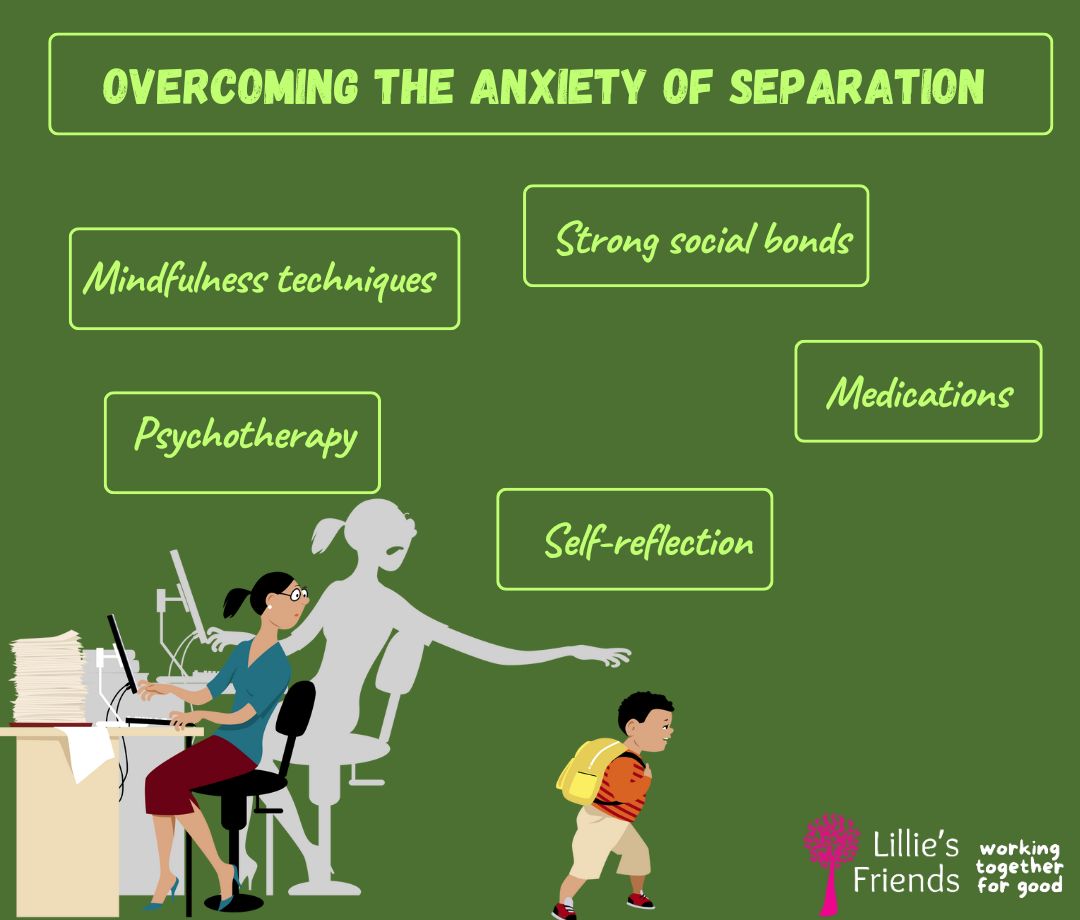
Adult Separation Anxiety Disorder Treatment Options
Consider getting professional assistance if you think you may be experiencing or developing separation anxiety disorder. You can only get over separation anxiety with the assistance of a trained specialist. They will create a customized online treatment plan for anxiety that may involve both non-pharmacological and pharmaceutical interventions.
Psychotherapy
There are several forms of psychotherapy that can assist you in overcoming separation anxiety:
- CBT, or cognitive-behavioral treatment. This type of treatment assists in recognizing harmful thought patterns and separation-related behaviors. It is beneficial to question these ideas and create more constructive coping mechanisms.
- DBT, or dialectical behavioral treatment. DBT, which has its roots in CBT, emphasizes transformation and acceptance. It works especially well for people who have strong emotional reactions.
- Group counseling. People may express their emotions and experiences while they are in a group environment. They learn they are not alone in their challenges thanks to this network of support.
- Family counseling. Given that SAD may affect family relations, involving family members in treatment sessions helps foster understanding and a supportive atmosphere.
Treatment with Medication
Although the FDA has not authorized any drugs especially for SAD, the following drug classifications may be useful:
- Medications for depression. Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) such as Effexor (venlafaxine) and Cymbalta (duloxetine) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as Prozac (fluoxetine) or Zoloft (sertraline) may be helpful.
- Drugs that reduce anxiety. Although benzodiazepines, such Xanax (alprazolam), Ativan (lorazepam), or Valium (diazepam), might provide temporary relief, they are often taken with care because of the possibility of dependency and adverse consequences.
- Beta-blockers. Some of the physical symptoms of anxiety can be controlled with the use of these drugs. Lopressor (metoprolol), Tenormin (atenolol), Inderal (propranolol), and Carvedilol (carvedilol) are a few well-known beta-blockers.
How Can Adults Avoid Separation Anxiety Disorder?
In order to manage separation anxiety, your doctor may first suggest self-help methods and psychotherapy rather than medication if your symptoms are minor. For further support, it is recommended to seek professional advice if the symptoms intensify. Here are a few useful and efficient strategies for dealing with separation anxiety.
Tip #1: Engage in Mindfulness
Your anxieties and perceived dangers are what anxiety feeds on. You give worry the chance to take control of you whenever you dwell on your fears. Use mindfulness practices to help you focus on the present moment in order to overcome separation anxiety. These methods also help you stay grounded and prevent your thoughts from getting out of hand.
Tip #2: Make Use of Transitional Items
Tangible artifacts that symbolize a loved one or connection are known as transitional objects. You will feel closer to the individual and more connected if you keep these items with you. You may wear a friendship bracelet, for instance, anytime you’re feeling nervous. Despite the distance between you, it could help you relax.
Tip #3: Examine Unsettling Ideas
By intentionally separating your nervous thoughts, you may practice this technique. For example, you can decide to categorize and separate your thoughts if you observe that you’re anxious about breaking up with someone. Make a conscious decision not to become anxious and examine your responses and presence in the present.
Tip #4: Engage in Conversation
SAD may make you feel isolated, just like a lot of other mental illnesses. Ask someone to share your sentiments with you if you feel like they are becoming too much to handle. Most of the time, just sharing may help you feel better. In order to assist you get over these emotions, the other person could also give you advise.
Takeout
In the end, it’s critical to acknowledge the parallels between separation anxiety disorder and other mental health issues. Like many of these other disorders, there might be disastrous outcomes if you don’t get care. Your everyday life and relationships may suffer greatly if you don’t get treatment for separation anxiety.
Thankfully, there are things you can do to manage separation anxiety and enhance your quality of life if you catch it early. Try some of the coping mechanisms listed above and get professional assistance if you think you may have separation anxiety disorder.
Faq
What are the three stages of separation anxiety?
The three stages of separation anxiety in adulthood are as follows:
- Protest—which is typified by sobbing and opposing division.
- Despair—characterized by melancholy and retreat when the attachment figure is not present.
- Detachment—the individual seems to adapt and interact with others, but frequently with less zeal or confidence.
What triggers separation anxiety?
The fear of being separated from a key attachment figure or a familiar setting sets off separation anxiety, which is frequently brought on by a sense of danger or the attachment to that person or location. Environmental changes, traumatic experiences, and genetic and environmental vulnerabilities are examples of factors. Regaining harmony and balance in your life may begin with getting therapy for separation anxiety.
Who is most likely to show signs of separation anxiety?
Separation anxiety is most frequently linked to infants and toddlers. However, adults may also experience separation anxiety, especially in the face of major life transitions or challenges.
Is separation anxiety normal in adults?
Indeed, adults often experience some degree of separation anxiety, particularly during significant life transitions or stressful situations. It could be a sign of a separation anxiety disorder, though, if it persists for a long time or significantly interferes with day-to-day functioning. You may work on separation anxiety and discover useful coping mechanisms by speaking with a healthcare professional.











