Adults typically require seven to nine hours of sleep. But according to a third of Americans↗, they don’t get as much sleep as is advised. Insomnia is the inability to get to sleep, stay asleep, or wake up too early and not be able to fall back asleep.
Stressful events might induce acute insomnia that lasts for a few days or weeks. So what is persistent insomnia? Chronic insomnia disorder may be suspected if sleep deprivation persists for at least three months and happens more than three evenings per week.
Which Chronic Insomnia Types Exist?
There are two types of chronic insomnia: primary and secondary. Although the exact etiology of primary insomnia is unknown, scientists believe it is connected to chemical alterations in the brain. To learn more about the origins of primary insomnia, researchers investigate this disorder using sophisticated MRI brain scans. Life circumstances and underlying medical issues↗ might cause secondary insomnia. Let’s go over common explanations in greater depth.
What Leads to Prolonged Sleeplessness?
Chronic insomnia can have various causes, including:
Way of life
- Life transitions and stressful circumstances
- Insufficient physical exercise
- Taking frequent naps throughout the day
- Sleeping irregular hours
- Frequent time zone shifts that result in jet lag
- Taking on various shifts, such as early or late shifts
- Eating too much in the evening
Health issues
- Mental health conditions, such as bipolar disorder, anxiety, and depression.
- Health issues (diabetes, asthma, persistent pain, endocrine disorders, etc.)
- Sleep-related conditions, such as sleep apnea and restless legs syndrome.
Stimulants and medications
- Particular antidepressants
- Laxatives
- Illegal substances
- Diuretics
- Inducing
- Coffee
- Alcohol
- Nicotine
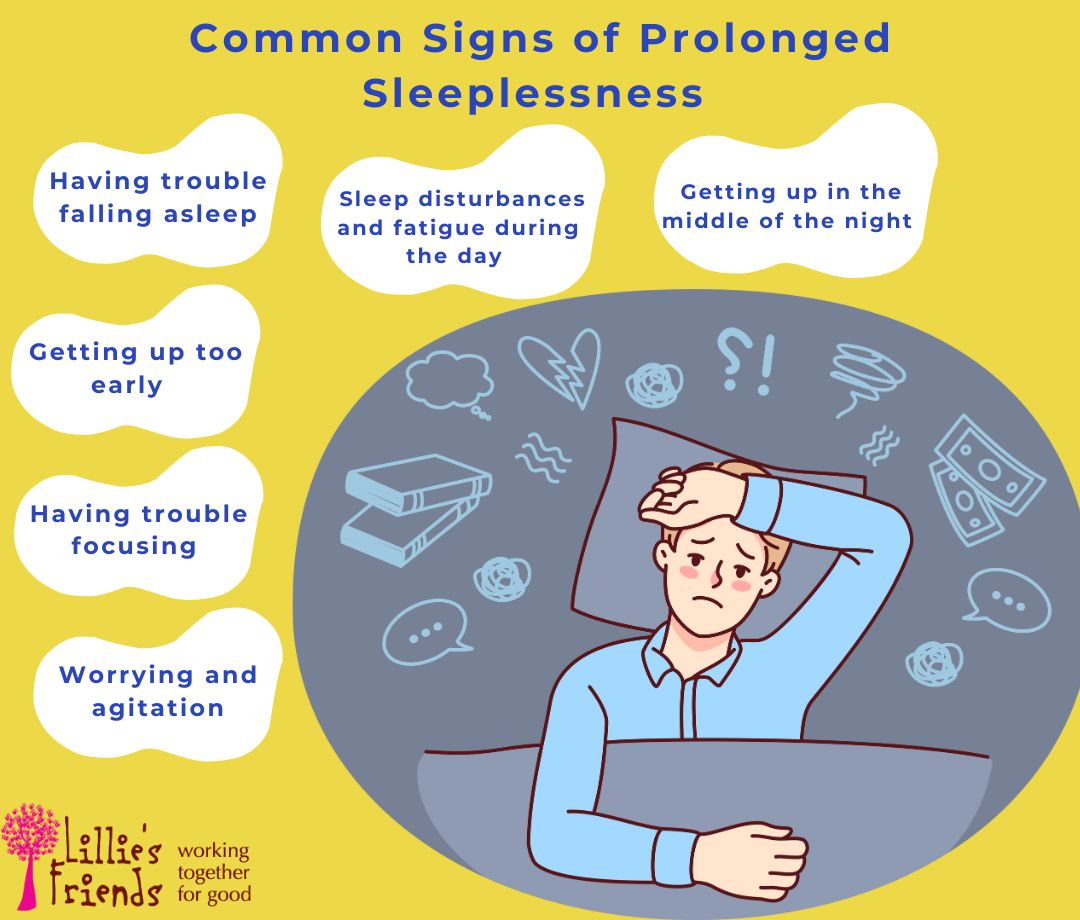
Symptoms of Chronic Sleeplessness
The following symptoms may be present in people with a chronic insomnia diagnosis:
- Having trouble falling asleep
- Getting up early
- Getting up in the middle of the night
- The inability to fall or keep asleep
- After waking up, feeling drowsy and exhausted
- The inability to take a daytime sleep, despite being exhausted
- Persistent exhaustion
- Experiencing irritation, sadness, or anxiety
- Inadequate memory, inability to focus and pay attention
- An increase in errors and mishaps
How Can Chronic Insomnia Be Treated?
Chronic insomnia is treated individually based on the underlying reasons and particular symptoms. Therapy, medicine, or a mix of several therapies might be part of it.
- CBT, or cognitive behavioral treatment. CBT has been shown to be successful in treating persistent insomnia, according to the research↗. It enables you to comprehend how your daily life is impacted by your sleeping patterns. You may learn how to alter your habits to improve your quality of sleep. There are CBT-I methods designed especially to treat insomnia.
- Drugs. The market offers various over-the-counter (OTC) sleep aids (melatonin, diphenhydramine, etc.) and prescription drugs (zolpidem, eszopiclone, zaleplon, etc.). They facilitate a quicker slumber.
Before taking them, you should discuss with your doctor the use of over-the-counter sleep aids, such as valerian root, chamomile tea, and others, for persistent insomnia. You can prevent adverse effects or drug interactions by scheduling a consultation.
Treating the underlying medical issue, such as acid reflux or persistent discomfort, may resolve your chronic sleeplessness.
7 Self-Help Strategies for Prolonged Sleeplessness
Additionally helpful are the following straightforward yet efficient home remedy guidelines:
- Steer clear of excessive alcohol and nicotine use.
- Engage in regular exercise.
- Cut back on midday naps.
- Limit your intake of caffeine, particularly in the afternoon.
- Don’t eat too much just before bed.
- Establish a cozy, dark sleeping space with a suitable temperature.
- Establish regular sleep schedules; designate certain times for bedtime and wake-up times.
The bottom line
Everyone has restless nights, but avoiding serious insomnia requires paying close attention to your health. Keep track of your symptoms, and get the assistance you require from clinic specialists if any of them begin to negatively impact you.











