Medical Disclaimer
The medicines listed on this website are only there to give you knowledge. Just because they are on the list doesn’t mean that anyone will be given them; in the end, treatment decisions are up to the healthcare workers. The medicines on this list are not all of them. Doctors may recommend other drugs, even ones that don’t contain stimulants, depending on the patient’s specific health needs and circumstances. Read more
Anxiety disorders may be crippling, making it impossible for a person to function normally in daily life. Thankfully, there are efficient therapies out there that may provide much-needed comfort, including Xanax. For many years, doctors have recommended Xanax, a fast-acting benzodiazepine, to treat patients’ anxiety and panic symptoms.
It can treat anxiety, but long-term use can be dangerous. We shall examine more closely the usage, dosage, and other aspects of Xanax in this post. We’ll also look at pharmacological options that could reduce anxiety without carrying the same hazards as taking Xanax.
What is Xanax used for?
Alprazolam is the medicine sold under the brand name Xanax. It’s a benzodiazepine medication with a fast-acting sedative action. Doctors often prescribe Xanax to treat panic and anxiety disorders, anxiety attacks, and sleep issues.
How Do You Take Xanax?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a neurotransmitter that is active in the brain, and Xanax acts by increasing its activity. By sending fewer electrical messages to brain cells, this neurotransmitter lowers their activity. Therefore, using Xanax leads to a higher level of GABA, which causes the calming effect.
Uses of Xanax
The FDA has authorised Xanax especially for the short-term treatment of:
- Anxiety is a condition that is generalised (GAD). Excessive concern and anxiety about various everyday issues, including job, family, money, and health, are hallmarks of generalised anxiety disorder (GAD). These feelings may last anywhere from a few months to years. In the short term, doctors prescribe Xanax to treat acute symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder (GAD), such as restlessness, impatience, and difficulty focusing. Long-term benzodiazepine usage, such as taking Xanax, may result in dependency and tolerance.
- Disorders related to panic. Panic attacks, which are frequent and abrupt experiences of extreme terror accompanied by physical symptoms, are the hallmark of this illness. By lessening the frequency and intensity of panic episodes, Xanax helps people reclaim control over their lives.
Off-label use of Xanax is also permitted for the following conditions:
- Depression. Although Xanax is not regarded as a first-line therapy for depression, in some circumstances it may both reduce anxiety related to the illness and elevate mood ↗.
- Sleeplessness. One may administer Xanax for the short-term treatment of insomnia, a sleep disorder characterised by trouble falling or staying asleep. In particular, it may benefit those who are suffering from acute anxiety that is interfering with their ability to fall asleep by helping to induce sleep ↗and enhance the quality of their sleep.
- Disordered anxiety. Xanax may be used to treat a number of symptoms ↗, including social anxiety, flushing, perspiration, and trouble speaking in front of others.
- There may be fear associated with the procedure. Anxiety brought on by dental or medical treatments ↗ may be managed with Xanax. To assist patients in feeling more at ease and comfortable before a surgical treatment or tooth extraction, for instance, it may be given as a premedication.
- Spastic contractions of muscles. For muscular spasms brought on by diseases like multiple sclerosis or other neurological illnesses, It works by causing the muscles to relax, therefore lessening the intensity and frequency of spasms.
- IBS is a syndrome of the irritable bowel. Xanax may assist in the management of IBS symptoms ↗, including diarrhoea, bloating, and stomach pain.
- Alcohol detoxification. Doctors may prescribe Xanax in conjunction with a monitored alcohol withdrawal protocol ↗. Detoxification may be safer when it helps to reduce withdrawal symptoms, including anxiety, tremors, and seizures.
Only the circumstances for which Xanax is authorised by a licensed healthcare professional and as recommended by them should be treated with this medication. It is a strong drug with a significant risk of addiction and abuse, and improper or continuous usage may have detrimental effects on one’s health. It must be taken under medical supervision at all times, and adjustments to the dose or length of use must be made with a healthcare provider’s advice.
Xanax for Nervousness
Xanax may be useful in treating anxiety symptoms rapidly and acutely. It aids in easing anxiety, restlessness, irritability, and panic attack symptoms. It lessens the intensity of symptoms and improves the person’s ability to go about their everyday life when taken as directed and well tolerated.
Xanax’s ability to treat anxiety
Peak effects of Xanax usually happen one to two hours after taking the drug. It acts swiftly. Several hours may pass before the effects wear off, depending on the person and the recommended dosage. Both immediate-release and extended-release forms of Xanax are available, enabling more accurate dosage and effects that last longer.
Although Xanax may be useful ↗ in treating severe anxiety symptoms, it is not a treatment for the condition. It’s critical to treat the underlying causes of anxiety as well, using medication, lifestyle modifications, and treatment as necessary.
Xanax for Anxiety Episodes
Because Xanax takes action quickly, it may be useful in treating panic attack symptoms. Panic attacks are brief, powerful bursts of worry or dread. Physical signs, including sweating, trembling, and chest discomfort, are often present.
Xanax’s efficacy in treating panic attacks
Taking Xanax as prescribed by a physician may help ↗ manage symptoms of panic disorder and stop panic episodes from becoming worse. This drug has the advantage of acting rapidly; after taking a dosage, it usually starts to work within 30 to 60 minutes. The medication may be very useful for controlling the unexpected start of panic episodes and rapidly reducing symptoms.

How Should Xanax Be Taken?
The most important thing while using Xanax, if you need it, is to pay close attention to the dose and use guidelines. Medication safety and efficacy can only be guaranteed by this method. While there are a few broad guidelines covered here, you should always speak with your prescribing physician to learn the details of your treatment regimen.
When Should I Take Xanax?
Patients should strictly follow their physician’s instructions when taking Xanax to minimise potential side effects. Depending on the demands and symptoms of each person, the intake time and frequency may vary. Generally speaking, dosages for Xanax should be spread out evenly throughout the day and should not exceed three times a day. To keep Xanax levels in the body constant, it is advised to take the medicine at the same time every day.
Comparing the Doses of Xanax for Panic Attacks and Anxiety
| Situation | Beginning dosage | Maximum amount must be taken each day |
| Anxiety | 0.5 to 0.25 milligrams three times each day | 4 milligrams daily |
| Panic Attacks | 0.5 to 1 milligram every three hours | 10 milligrams daily |
The likelihood of adverse effects might rise with higher Xanax dosages.
Risks and Side Effects of Xanax
The side effects of Xanax might differ from person to person. Some people deal with severe or uncommon consequences, while others do not experience them at all. Furthermore, there is a significant risk of misuse with Xanax.
Typical Adverse Reactions to Xanax Use
Use of Xanax requires careful observation, treatment, and consideration of the following symptoms:
- Headache
- Lightheadedness
- Tiredness
- Constipation
- Vertigo and queasiness
- Parched lips
- Hazy vision
- Modifications in hunger or weight gain or loss
- Having problems urinating
- Issues with memory
- Variations in mood
- Modifications in sexual desire and behavior
If you have questions about Xanax or experience any side effects, consult your doctor. They may help you manage side effects, reduce the likelihood of experiencing them, adjust your dosage, or select an alternative effective treatment plan.
Long-Term Dangers and Abuse Potential
The potential for dependency and addiction is one of the most important long-term dangers associated with Xanax usage. When a drug is used over an extended period of time, the body may get used to its effects and need larger dosages to provide the same degree of symptom alleviation. Stopping the medicine suddenly could lead to withdrawal symptoms and physical dependency.
Long-term Xanax usage may raise the risk of dependency as well as cognitive impairment, memory difficulties, and falls and accidents due to balance and coordination problems.
Abuse of drugs is another concern. As a depressant of the central nervous system, Xanax causes relaxation and euphoria in some individuals. These properties may make it more enticing for usage as a recreational or self-medication tool. There is a risk of dependency, addiction, and overdose when using Xanax for non-medical reasons.
Use Xanax as suggested by your doctor and at the recommended doses to reduce the dangers connected with using the medicine. Monitoring your symptoms and discussing any concerns or potential negative effects is crucial. Thanks to online anxiety therapy, it is now even more accessible since you may speak with your doctor right away and obtain the instructions you need from the comfort of your own home.
Additionally, be mindful of possible drug interactions with vitamins, other prescriptions, and other drugs. Tell your doctor about all the drugs and supplements you take to be sure Xanax is the best and safest treatment. In some situations, your doctor may advise you to use other therapies or treatments in addition to or instead of Xanax.
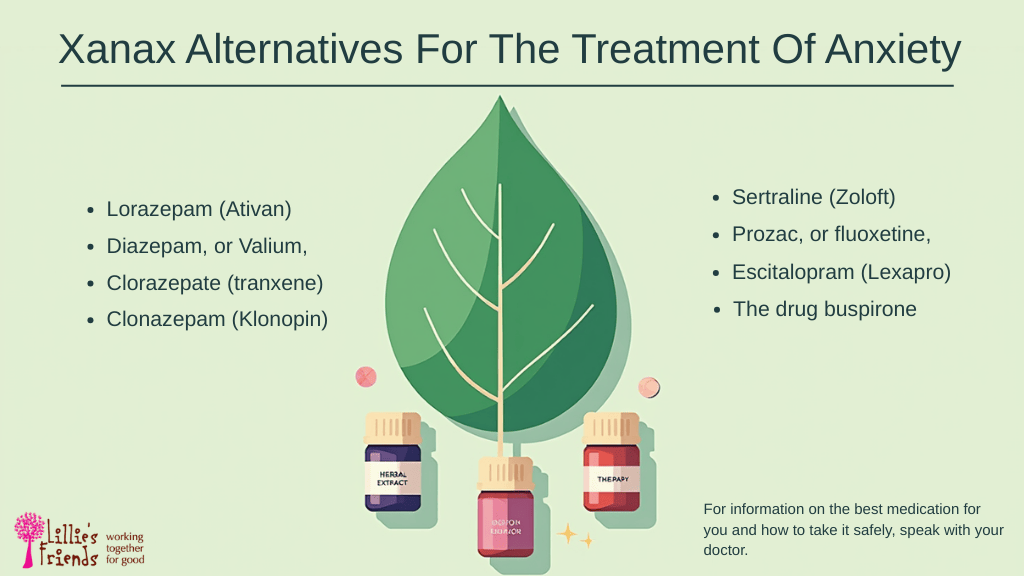
Xanax substitutes for anxiety
Some people can’t take or tolerate Xanax for various reasons. Thankfully, there are several good substitutes available:
- Additional benzodiazepines. Besides Xanax, physicians also prescribe other benzodiazepines for anxiety disorders. The FDA has authorized Ativan (lorazepam), Valium (diazepam), Tranxene (clorazepate), and oxazepam, among other medications in this class, for treating anxiety in the short term. Panic disorder is a condition for which Klonopin (clonazepam) is authorized. To choose which benzodiazepine is best for their patients, physicians often weigh symptoms and ailments like depression and sleeplessness that are frequently linked to anxiety when deciding between Xanax and other benzodiazepines.
- Medicines used to treat depression. Antidepressants are often used to treat depressive symptoms, but they are also useful in the treatment of anxiety disorders. The two classes of antidepressants that are most often given for anxiety are serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). They function by raising norepinephrine and serotonin levels in the brain, which helps lessen the sensations of anxiety. They may induce adverse effects, including nausea or sleepiness, and take several weeks to start functioning.
- Buspirone. An anti-anxiety drug called buspirone is often used in place of Xanax. It works by raising serotonin levels in the brain. Raising the amounts of this neurotransmitter may help lower anxiety since it plays a role in mood regulation. Buspirone does not make you drowsy as Xanax does, and it is not addictive. It may take many weeks for it to start functioning, and it is usually taken twice or three times a day.
- Beta-blockers are a type of medication. In addition to being used to treat high blood pressure, beta-blockers may also be utilized to alleviate anxiety symptoms. They function by preventing the hormone adrenaline’s effects, which are produced during the “fight or flight” reaction. Beta-blockers help lessen the physical signs of anxiety, such as trembling or a speeding pulse, by inhibiting the release of adrenaline. They have no impact on the mental symptoms of anxiety, including dread or concern.
Additionally, there are a number of non-pharmacological substitutes for Xanax that may effectively manage symptoms without the dangers or adverse effects:
- Psychoanalysis. Talk therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) may assist patients in recognizing harmful thinking patterns and developing coping mechanisms for anxiety management.
- Mindfulness and meditation. By using these methods, people may learn to regulate their anxiety symptoms by being more present-focused. Stress reduction and GAD therapy have been shown to benefit from mindfulness meditation ↗.
- Modifications in lifestyle. Enhancing mental health and lowering anxiety levels may be achieved by regular exercise, a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and abstaining from alcohol, caffeine, and nicotine. Maintaining your physical health might benefit your mental health as well.
- Additives. Anxiety symptoms may be effectively managed by using certain natural remedies, such as lavender, passionflower, and valerian root. To prevent medication interactions, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Not every Xanax substitute is effective for every person. To discover the ideal mix of therapies that will work for you, some trial and error may be necessary.
In summary, does Xanax effectively treat anxiety and panic attacks?
Anxiety may be effectively treated with Xanax. Additionally, Xanax may prevent panic episodes, offering prompt relief when it’s most required. However, due to the possibility of dependence and addiction with continued usage, this drug should only be administered under strict supervision.
Speak with a healthcare professional to find the right course of action for your situation. For the treatment of anxiety, you may obtain prescribed Xanax or other medications online. During follow-up sessions, you can get ongoing assistance and symptom monitoring. To identify the best course of action for you, ask for assistance and consider all of your alternatives for therapy.
FAQ
What Are the Signs of Addiction to Xanax?
Increased tolerance, withdrawal symptoms when the drug is stopped, trouble managing Xanax usage, and persistent use despite unfavorable effects are all indicators of Xanax addiction. Additional indicators might include a decline in social interaction, behavioral or emotional changes, and responsibility neglect. Seek assistance from a licensed healthcare professional or addiction expert if you or someone you know is exhibiting these symptoms.
Is Xanax Good for Test Anxiety?
Because it helps lessen the psychological and physical symptoms of anxiety, such as restlessness, irritability, and nervousness, Xanax is useful in treating test anxiety. If you’re not sure whether Xanax will work for you, go to your doctor.
Is Xanax the First-line Treatment for Anxiety?
While Xanax is an effective symptom reliever for anxiety, it is not a cure for anxiety. Xanax doesn’t treat the fundamental causes of the problem; it may only provide momentary comfort. A doctor may suggest a mix of medication, therapy, and lifestyle modifications for the long-term treatment of anxiety.
Can Xanax Cure Anxiety?
Anxiety may be effectively treated with Xanax. Additionally, Xanax may prevent panic episodes, offering prompt relief when it’s most required. However, due to the possibility of dependence and addiction with continued usage, this drug should only be administered under strict supervision.
Speak with a healthcare professional to find the right course of action for your situation. For the treatment of anxiety, you may obtain prescribed Xanax or other medications online. During follow-up sessions, you can get ongoing assistance and symptom monitoring. To identify the best course of action for you, ask for assistance and consider all of your alternatives for therapy.











