ADHD stands for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Avoid letting ADHD define who you are. Rethink it with the appropriate backing.
Get individualized ADHD treatment that fits in with your daily schedule. Allow experts to help you focus better and feel better.
To put it simply, what is ADHD?
The mental health illness known as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) can impact both adults and children. It is characterized by impulsivity, hyperactivity, and persistent inattention, which can affect relationships, everyday activities, and general quality of life. People with ADHD may exhibit restless behaviors, have trouble focusing for extended periods of time, or make snap decisions without thinking through the repercussions.
What Is the Frequency of ADHD?
Approximately one-third of kids with ADHD are still diagnosed as adults. It is estimated that between 2.6% and 6.8% of adults suffer from ADHD. However, since undiagnosed ADHD is still common in adults and many may have received a false diagnosis as children, this rate may be underreported.
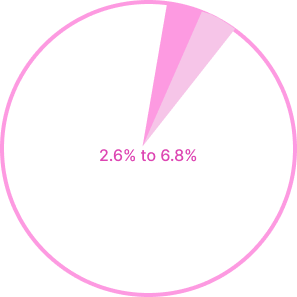
Comparing ADHD and ADD: Dispelling the Myths
ADHD
According to modern medical terminology, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, or ADHD, is a condition marked by a combination of impulsive behavior, hyperactivity, and a persistent inability to maintain focus. ADHD is defined as more than just a childhood disorder; it can manifest in a variety of ways throughout adolescence and adulthood.
ADD
Originally used to refer to attention problems without hyperactivity, this term now stands for attention deficit disorder. ADD is no longer a distinct diagnosis, though, as it has been categorized as part of ADHD in recent medical literature. A more comprehensive term that more accurately describes the spectrum of symptoms is ADHD.
ADHD types
There are various ways that attention deficit hyperactivity disorder presents itself, and each has its own difficulties and traits:

Presentation that is primarily inattentive
Not very hyperactive, but having trouble concentrating and completing tasks.
A combined presentation
a combination of symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity and inattention.
Mostly impulsive and hyperactive presentation
displaying less inattention and more impulsive and hyperactive behavior, which is characteristic of those with ADHD.
ADHD symptoms
Recognizing and treating ADHD requires an understanding of its symptoms. ADHD refers to symptoms that typically fall into two main categories: hyperactivity-impulsivity and inattention. These symptoms, which reflect the various characteristics of ADHD, can appear differently and vary in intensity in different people.

Typical traits of ADHD include:
Inattentiveness
- Having trouble focusing on duties or activities
- Frequently misplacing essential items
- Easily becoming sidetracked by unrelated stimuli
- Ignorance of everyday tasks
- Having trouble completing tasks or following directions
Hyperactivity and impulsivity
- Squirming in the seat, tapping hands or feet, or fidgeting
- The inability to remain seated when it's expected
- Experiencing restlessness
- nterrupting or encroaching on the activities or conversations of others
- Talking too much
ADHD causes
Although the precise cause of ADHD is unknown, knowing some of the possible contributing factors aids in understanding how this mental illness impacts day-to-day functioning. According to research, its development is influenced by a mix of neurological, environmental, and genetic factors.

Impact of Genetics
- Family background. ADHD frequently runs in families. Research suggests that the likelihood of developing the disorder is significantly influenced by genetics. ADHD has been associated with certain genes, especially those related to dopamine neurotransmission.
Structure and Function of the Brain
- Development of the brain. People with ADHD have been found to have differences in brain activity and development that impact their ability to pay attention and control themselves.
- Brain activity. According to these studies, individuals with ADHD exhibit differences in the structure and function of specific brain regions.
It’s critical to realize that ADHD is not caused by a single factor. Rather, it is probably a complex condition caused by a number of factors.
Risk Factors for ADHD
Although the precise causes of ADHD are numerous and complex, there are some risk factors that can raise the chance of getting moderate to severe ADHD.
Environmental Factors During Pregnancy and the Early Years
- Exposures during pregnancy. Pregnancy-related exposure to drugs like alcohol or tobacco may raise the likelihood that a child will grow up to have ADHD.
- An early birth. ADHD is more likely to develop in babies who are born prematurely or underweight.
- An early home environment that was inconsistent. Early childhood home environments that are extremely chaotic or unstable may be risk factors. Stressors or trauma experienced early in life may also raise the chance of developing ADHD.
- Exposure in the early years. ADHD symptoms may arise as a result of exposure to environmental pollutants, such as lead, which can be found in pipes and old paint.
- Nutritional considerations. Early childhood dietary patterns, especially those deficient in vital nutrients, may be associated with a higher risk of ADHD.
Psychosocial Components
- Social elements. elements like a lack of social support or social isolation during crucial stages of development.
- Persistent sleep deprivation. ADHD symptoms may be exacerbated by prolonged sleep deprivation during critical developmental stages.
Difficulties of Having ADHD
ADHD is more than just hyperactivity or attention problems. It can have profound effects on many facets of life, including relationships, employment, and education. In order to seek the right interventions and support, people with ADHD and their caregivers must be aware of these potential difficulties.
Academic and Professional Difficulties
- Studying is challenging. Focus, task organization, and assignment completion are common challenges for people with ADHD. Academic difficulties may arise if multiple symptoms of this category appear at once.
- Problems at work. Similar challenges may arise at work, impacting career advancement and job performance.
Relationship and Social Challenges
- Interpersonal connections. Due to disagreements and unintended outcomes from rash decisions, the impulsivity and hyperactivity linked to ADHD can strain interpersonal relationships.
- Social engagement. Misunderstandings and social isolation can result from difficulties focusing in social situations.
Issues with Mental Health
- Elevated risk for depression and anxiety. ADHD can exacerbate emotional and mental health issues by co-occurring with depression and anxiety disorders.
- Low regard for oneself. Low self-esteem and feelings of inadequacy can result from ongoing difficulties and setbacks.
Behavioural Problems
- Impulsivity as well as taking risks. Particularly in teenagers and young adults, ADHD can cause impulsive behavior that occasionally leads to dangerous or damaging activities.
- Substance misuse. Substance abuse and addiction are more likely to occur, perhaps as a coping strategy for the previously described symptoms of ADHD.
Effects on Lifestyle and Health
- Disruptions in sleep. Sleep issues are common in people with ADHD, which can worsen symptoms and have an impact on general health and well-being.
- Challenges related to lifestyle. Inattention and low energy levels can make it harder to manage daily routines and health habits, which can result in a variety of lifestyle-related problems.
Effective ADHD management necessitates a comprehensive strategy that takes into account both the main symptoms and any potential side effects. In order to provide comprehensive care, this approach entails the cooperation of supportive family members and friends as well as medical professionals, including mental health specialists.
ADHD Is Diagnosed In What Way?
A healthcare professional follows a methodical process to diagnose ADHD. It entails a thorough assessment of the developmental history, behaviors, and symptoms. Effective ADHD treatment requires a comprehensive and accurate assessment, which is ensured by this multi-step diagnostic procedure.

- Step 1: Compiling medical records
Gathering the patient’s behavioral history, symptoms, and experiences is the first step in the diagnostic process. The assessment is intended to cover a long period of time because some symptoms of ADHD should have been present since childhood.
- Step 2: Examining the results
In order to assess the severity of ADHD symptoms, patients respond to interviews and standardized questionnaires.
- Step 3: Verifying the diagnostic standards
assessing symptoms to determine whether they fit the criteria for an ADHD diagnosis using diagnostic manuals like the DSM-5.
- Step 4: Conducting medical examinations
In order to rule out any additional medical conditions, a mental health professional may occasionally refer a patient to a general practitioner.
- Step 5: Getting a medical diagnosis
Following the compilation and analysis of all gathered data to arrive at a thorough diagnosis, possible treatment options are examined.
Options for Treating ADHD
ADHD is usually treated using a mix of techniques based on each patient’s needs:
ADHD drugs
These include drugs that increase focus and decrease hyperactivity, such as stimulants or non-stimulants. They frequently accompany psychotherapy.
Psychoanalysis
To treat emotional and behavioral issues, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic modalities are employed.
Changes in lifestyle
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and an organized schedule can all greatly aid in the management of ADHD symptoms.
Community and family support
includes access to support groups for exchanging experiences and coping mechanisms, as well as training for parents and other caregivers.
Frequent observation
Over time, efficacy is ensured through ongoing evaluation and modification of the treatment strategy.
Is It Possible to Prevent ADHD?
The following actions may lower the likelihood or intensity of ADHD symptoms:
Risk factors for the development of ADHD can be decreased by maintaining good prenatal health and abstaining from drugs, alcohol, and tobacco during pregnancy.
Reducing exposure to environmental pollutants, especially during early childhood, may help reduce the likelihood of symptoms associated with ADHD.
Early detection of ADHD symptoms can aid in better management of the disorder and stop it from getting worse.
During pregnancy and the early years of life, a well-balanced diet full of vital nutrients may help lower the risk of ADHD.
ADHD risk may be decreased by reducing stress during pregnancy and in the early years of the child’s life.
In order to effectively manage ADHD, early detection and intervention are made possible by routine health examinations.
These actions do not ensure prevention, but they may help lower the likelihood or severity of ADHD. ADHD is a complicated disorder that is impacted by many different things.
When to Consult a Physician
The following are important signs that it’s time to see a doctor:
- A persistent lack of focus. It’s crucial to see a mental health professional if problems maintaining focus have a major influence on day-to-day activities, academic performance, or professional performance.
- Hyperactivity that interferes with day-to-day activities. A medical evaluation is necessary for noticeable and persistent hyperactive behavior, particularly when it interferes with everyday activities.
- Concerning behaviors that are impulsive. It is advised to have a professional evaluation if impulsive behaviors cause issues at work, school, or in relationships.
- Has trouble in a variety of situations. It’s time to consult a doctor when hyperactivity or attention problems are noticeable in a variety of settings, such as the workplace, school, or home.
- A detrimental effect on interpersonal relationships. When friends or family relationships are difficult to maintain because of ADHD symptoms, it’s time to think about getting professional help.
- Behavioral or emotional difficulties. A healthcare professional should be consulted if symptoms are accompanied by behavioral issues, mood swings, or emotional distress.
- Concerns voiced by those who are close. A referral to a healthcare professional may also be prompted by comments regarding behavioral or attentional problems made by friends, family, or coworkers.
- If earlier measures haven’t been successful. A medical expert can assist you in identifying appropriate methods if you’ve tried other tactics or interventions with little to no success.
Treatment results can be greatly enhanced by early diagnosis and intervention. Make an appointment with a healthcare professional for a thorough assessment if any of the aforementioned indicators seem to match your everyday experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is ADHD a form of autism?
ASD (autism spectrum disorder) and ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) are two different mental illnesses. It's crucial to visit a healthcare professional and obtain a precise diagnosis and suitable treatment plan because they can co-occur and share some symptoms.
Are there advantages to having ADHD?
People with ADHD can alter their perspective on certain symptoms, even though it is generally incorrect to discuss the benefits of having a disorder. For instance, hyperfocus may enable one to succeed in their areas of interest, daydreaming may enhance creativity, and having to cope with ADHD may increase flexibility and a propensity for original problem-solving. It's crucial to consult a healthcare provider if ADHD symptoms substantially disrupt daily life, though, as attitude and coping mechanisms alone cannot replace professional treatment.
What does ADHD feel like in adults?
Adults with ADHD may experience impulsivity, restlessness, persistent distractibility, difficulty focusing, trouble organizing tasks, and frequently a feeling of being overburdened by everyday obligations.
Is ADHD a mental disorder or a disability?
ADHD falls under the category of neurodevelopmental mental illness. When its symptoms substantially interfere with day-to-day functioning, it may be deemed a disability.
Can someone with ADHD lead a normal life?
With the help of self-help methods and mental health professionals, many people with an ADHD diagnosis manage their symptoms and lead happy, successful lives.
What is ADHD commonly mistaken for in adults?
Adult ADHD is frequently confused with bipolar disorder, depression, and anxiety disorders. It's critical to speak with a medical expert who can identify ADHD and rule out other illnesses.
